>> Why objectify analgesia <<
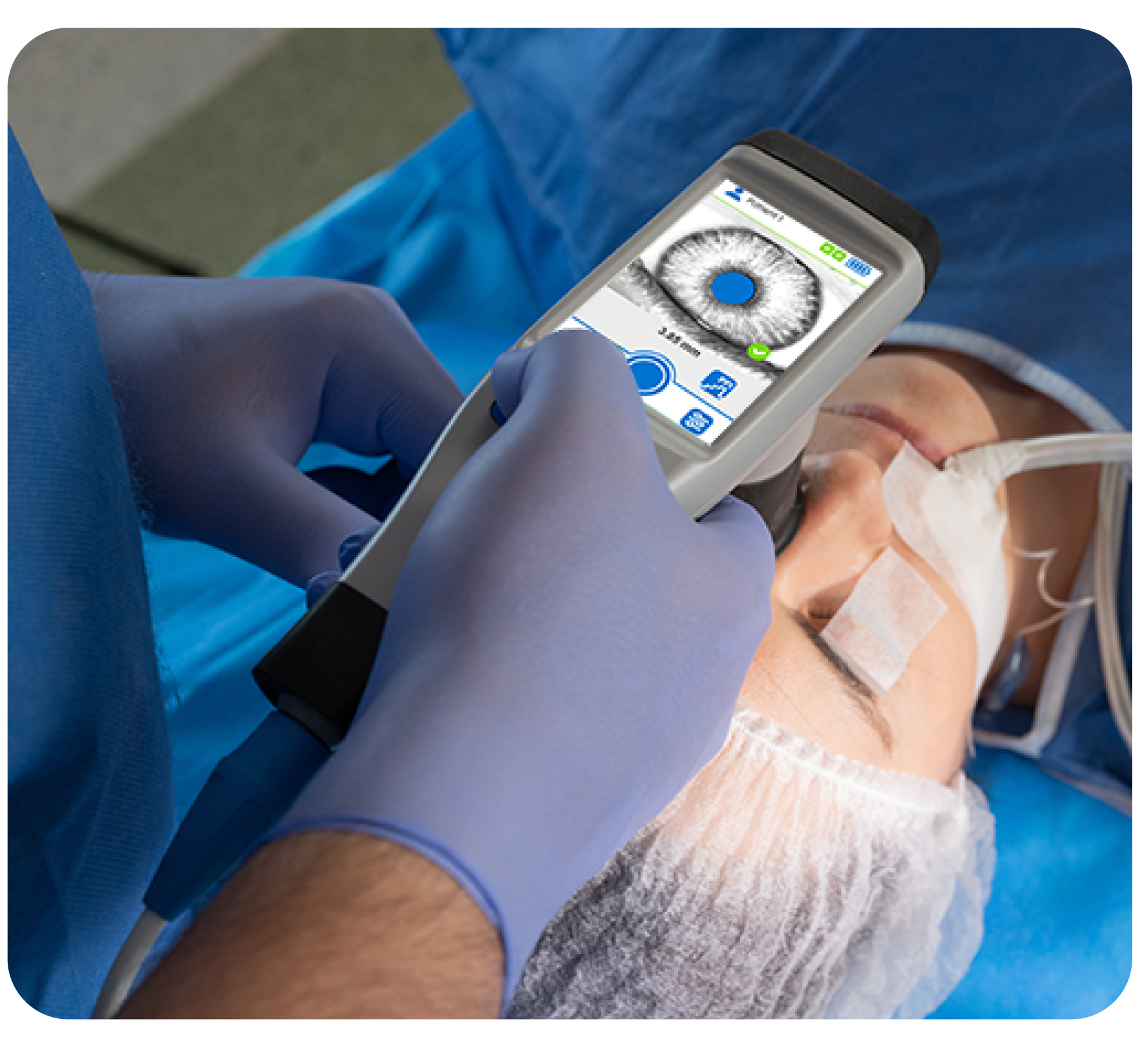
Analgesia is one of the three fundamental pillars in the management of anaesthetised or sedated patients.
Inadequate analgesia can lead to post-operative complications, excessive nociception and agitation.
Excessive analgesia can lead to undesirable effects such as hypotension, bradycardia, prolonged recovery times, nausea and vomiting, and morphine-related hyperalgesia.
It is therefore important to be able to assess the level of analgesia eobjectively, tailored to each individual patient.

Analgesia is one of the three fundamental pillars in the management of anaesthetised or sedated patients.
Inadequate analgesia can lead to post-operative complications, excessive nociception and agitation.
Excessive analgesia can lead to undesirable effects such as hypotension, bradycardia, prolonged recovery times, nausea and vomiting, and morphine-related hyperalgesia.
It is therefore important to be able to assess the level of analgesia eobjectively, tailored to each individual patient.
>> How to Measure Analgesia <<
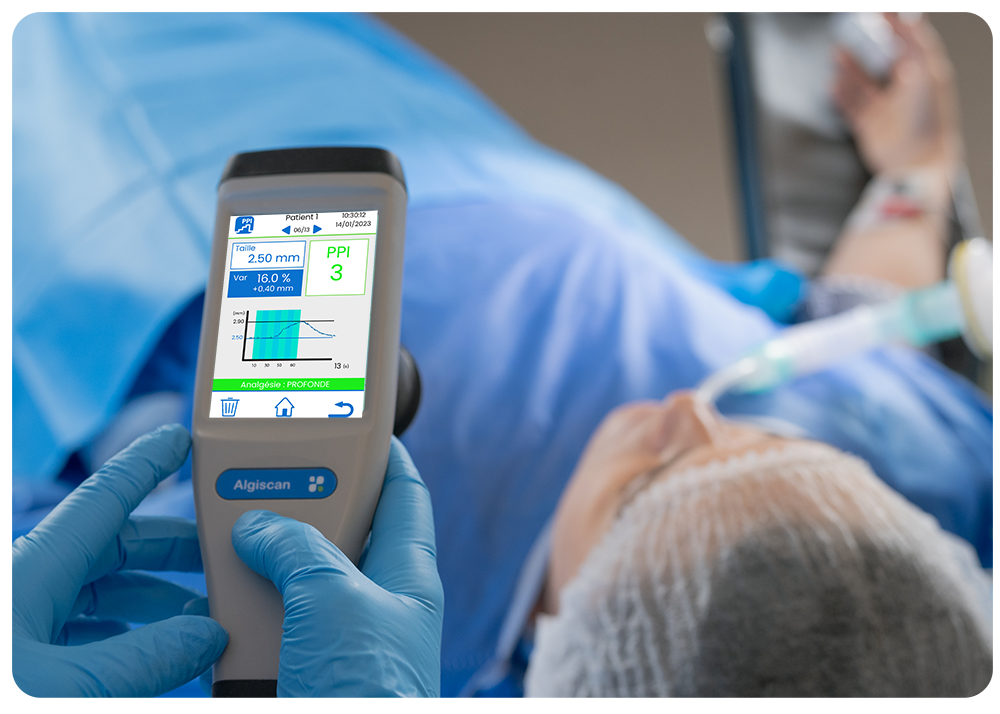
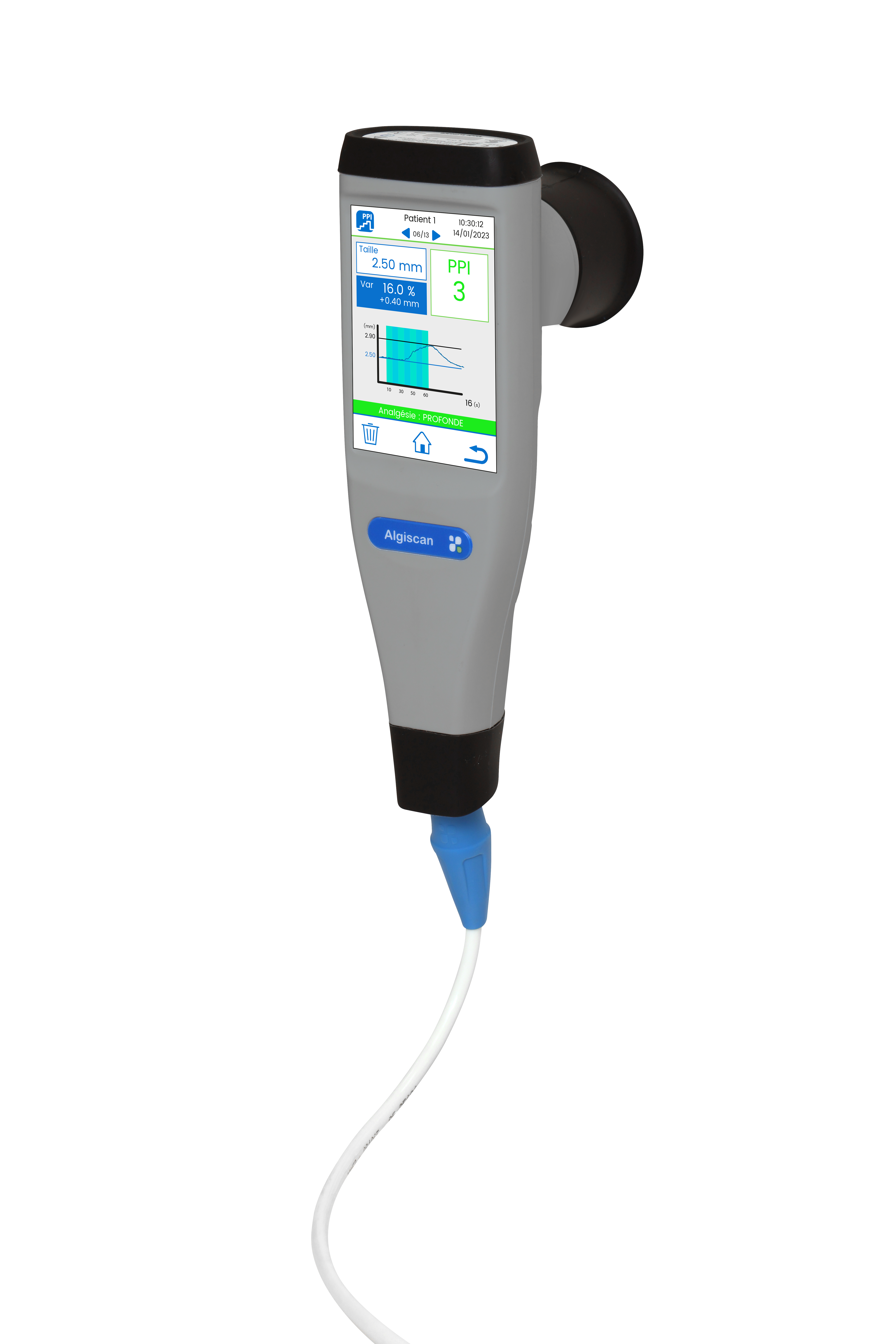
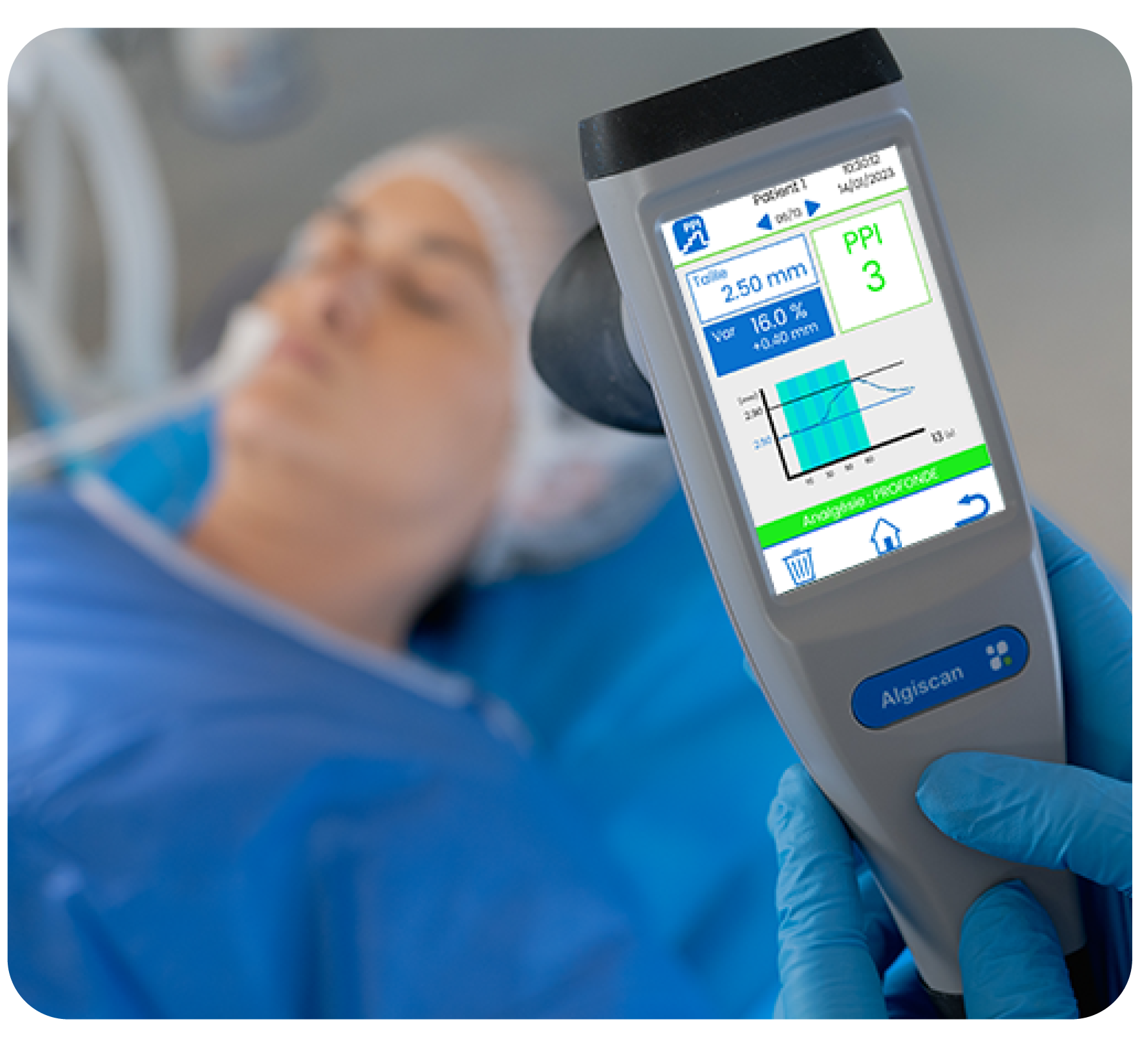
The AlgiScan delivers the Pupillary Pain Index (PPI), a score that reflects the patients’ level of analgesia.
The pupil is the most sensitive marker of nociception and has the particularity of being specific to nociception in case of unconscious patients. The PPI is calculated from pupillary dilation during increasing infra-nociceptive stimulation.
A higher PPI score (close to 9), indicates higher sensitivity to nociception and lower analgesia whereas a PPI score close to 1 indicates high analgesia.
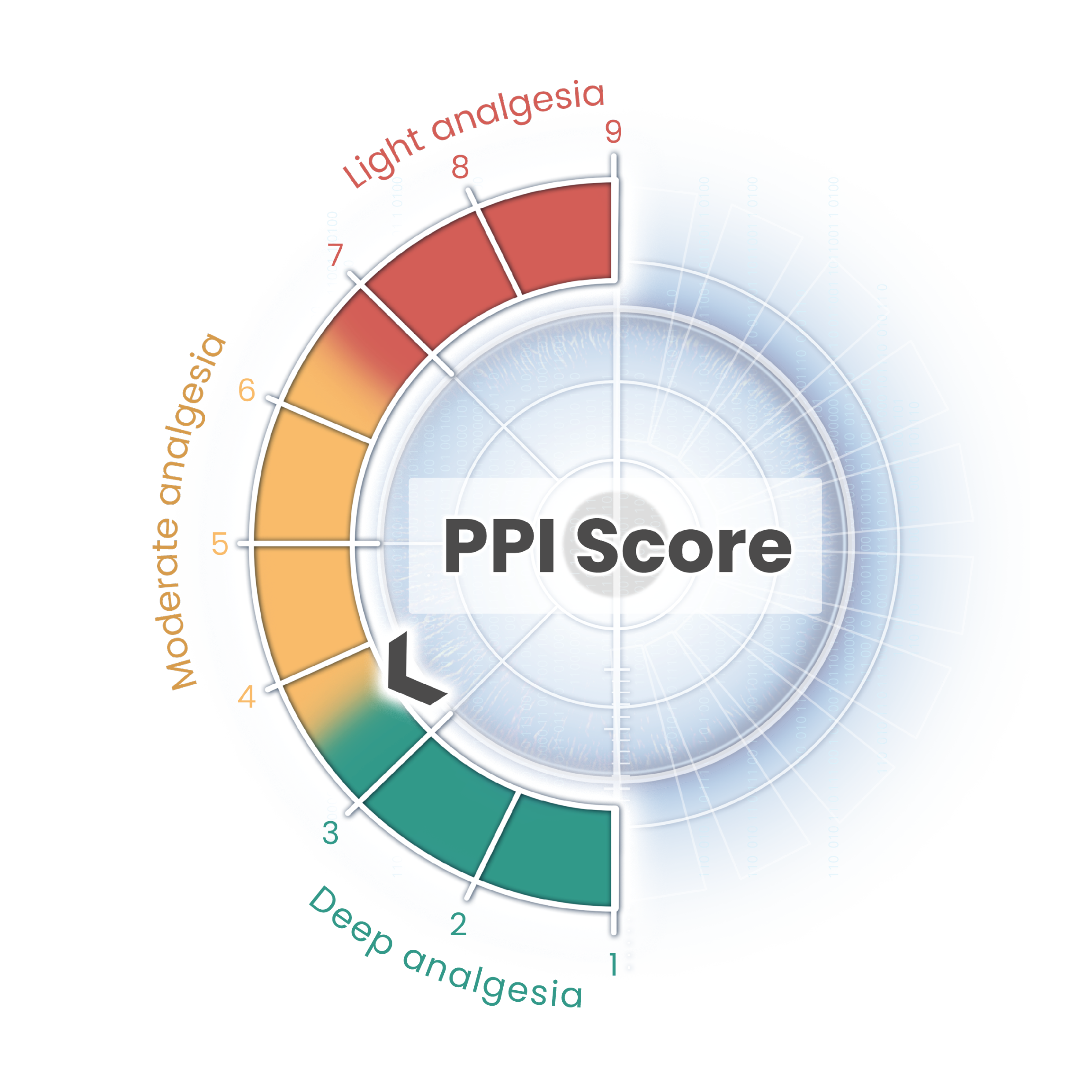

The Algiscan delivers the Pupillary Pain Index (PPI), a score that reflects the patients’ level of analgesia.
The pupil is the most sensitive marker of nociception and has the particularity of being specific to nociception in case of unconscious patients. The PPI is calculated from pupillary dilation during increasing infra-nociceptive stimulation.
A higher PPI score (close to 9), indicates higher sensitivity to nociception and lower analgesia whereas a PPI score close to 1 indicates high analgesia.
>> PPI score and AlgiScan <<
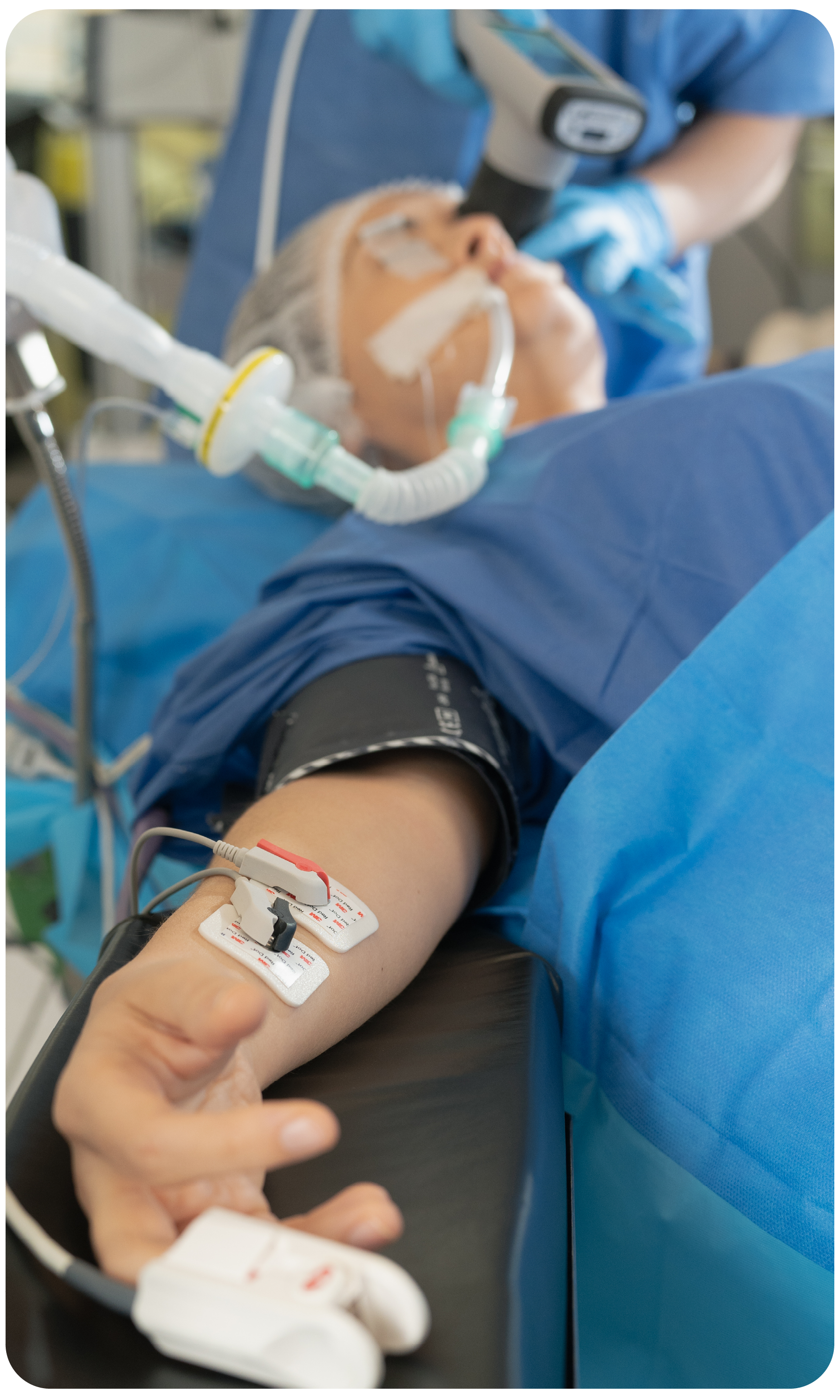
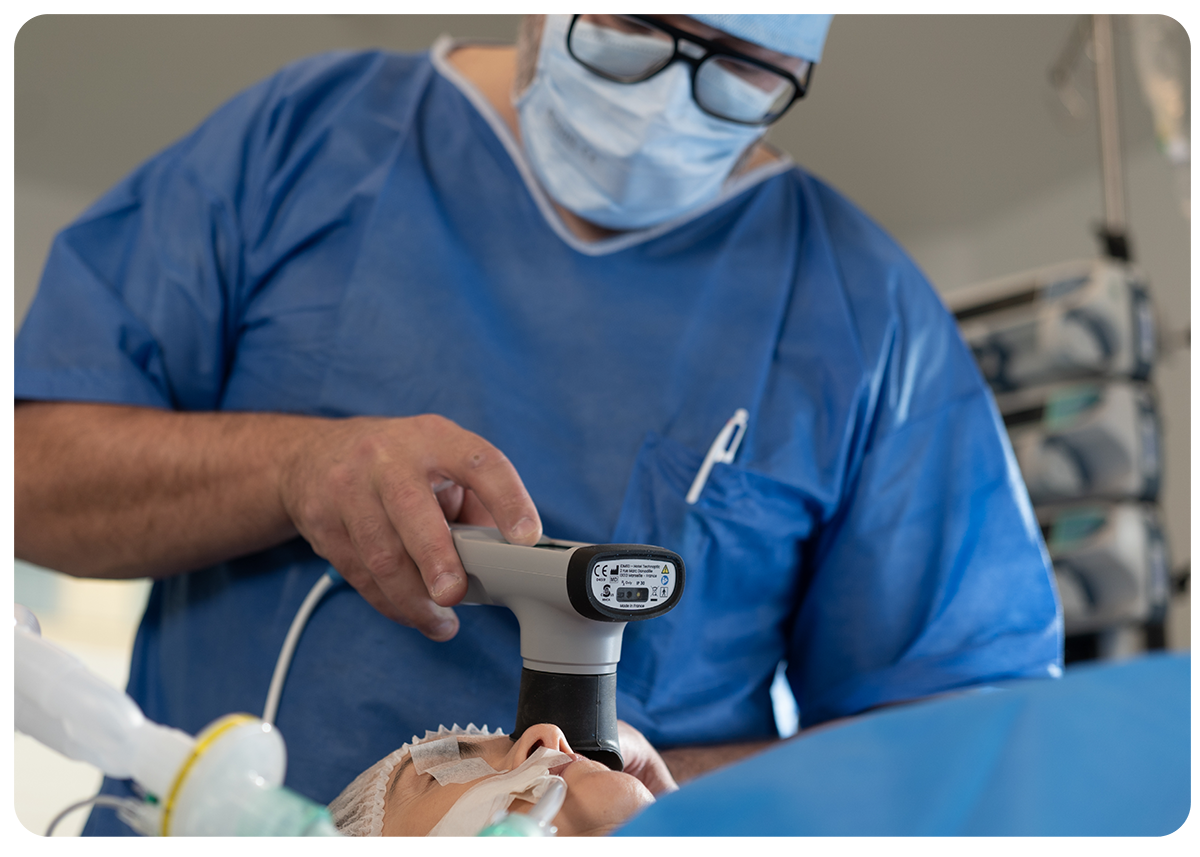
AlgiScan is a simple and non-invasive tool that enables anaesthesia and intensive care teams to optimise the management of nociception quickly and effectively.
AlgiScan’s PPI score can be used to anticipate the patient’s needs and make preventive therapeutic adjustments before any nociceptive stimulus.
By targeting a PPI score, anaesthesia and critical care teams can obtain an objective, personalised and predictive interpretation of their analgesia strategy implemented.

AlgiScan is a simple and non-invasive tool that enables anaesthesia and intensive care teams to optimise the management of nociception quickly and effectively.
AlgiScan’s PPI score can be used to anticipate the patient’s needs and make preventive therapeutic adjustments before any nociceptive stimulus.
By targeting a PPI score, anaesthesia and critical care teams can obtain an objective, personalised and predictive interpretation of their analgesia strategy implemented.
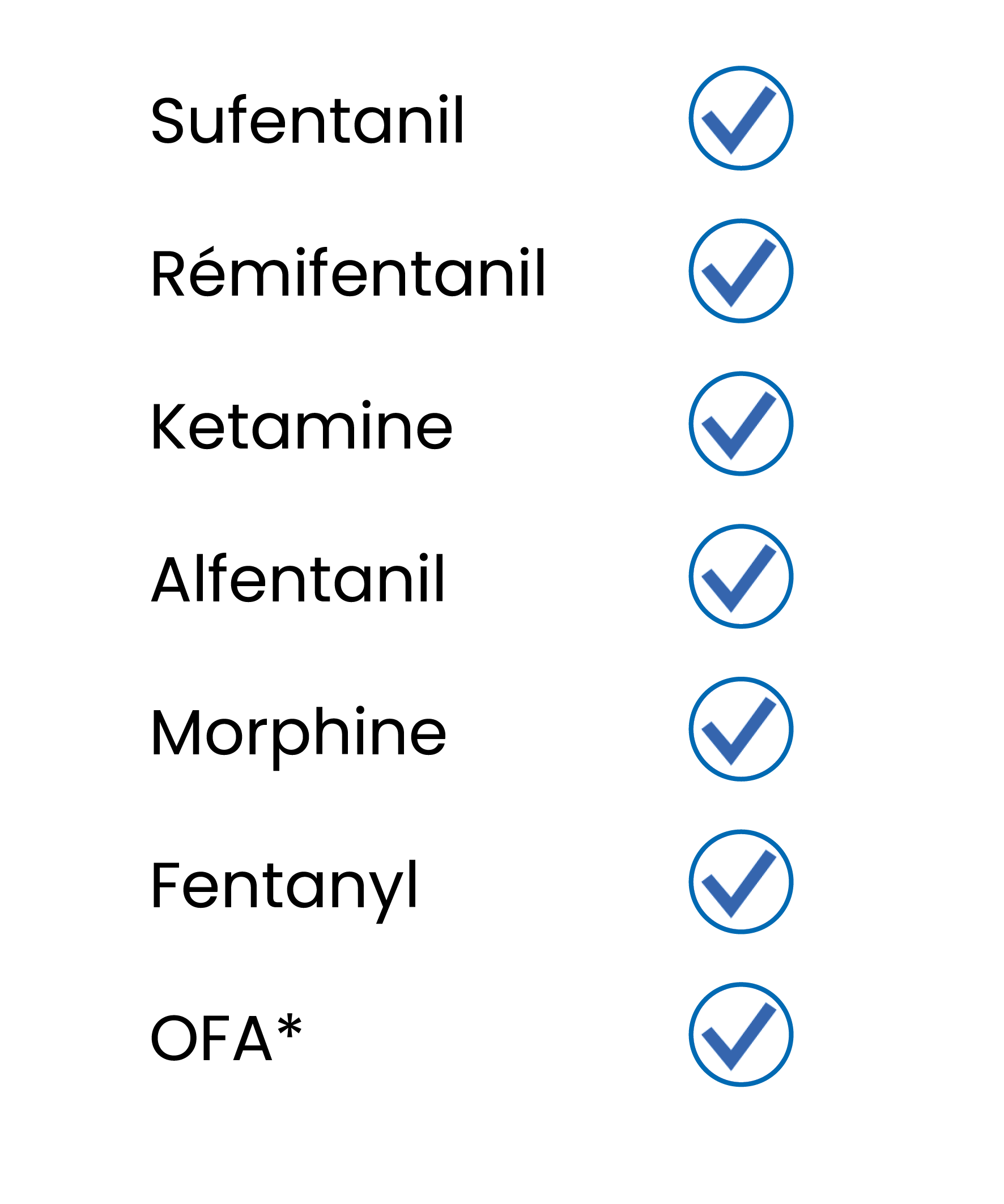
The PPI is independent of the anaesthesia technique used
Sufentanil
Rémifentanil
Kétamine
Alfentanil
Morphine
Fentanyl
OFA*
*Opiate-free anaesthesia
The PPI is independent of
the anaesthesia technique used

*Anesthésie sans opiacés
>> Individualise Analgesia <<
- Objectify the strategy in place
- Optimise analgesics doses
- Prevents under- and overdosing
>> Predictive measurement <<
- Predict the absence of nociceptive response
- Predict the nociception / anti nociception balance
- Anticipate the response to nociceptive stimuli
- Predict the absence of nociceptive response
- Predict the nociception / anti nociception balance
- Anticipate the response to nociceptive stimuli
>> Designed for OR, PACU and ICU<<
- SImple, objective et reproductible score
- Lightweight, mobile device for bedside use
- Reusable eyecup
vidéos
TESTIMONIALS
During our daily practice, we often come across paediatric patients who wake up agitated after anaesthesia, even when they are supposed to have received adequate intraoperative or postoperative analgesia. What attracted me to AlgiScan is its simplicity, portability (it can easily fit in one’s pocket), and user-friendly interface.
With AlgiScan, we now have the ability to predict the depth of analgesia in paediatric patients before extubating them.
I observed that in neurosurgical intensive care, patients with brain damage had very low PPI scores. This means that they were receiving an excessive amount of morphinics in relation to their actual analgesic needs. The integration of the PPI would allow for better adjustment of morphine doses, in order to ensure optimal analgesia without excess. Measurement of PPI can be a method to objectify nociception. The PPI makes it possible to link a state of agitation to a real lack of analgesia.
” What is not defined cannot be measured. What is not measured, cannot be improved ” (Peter Drucker / William Thomson). It is crucial to monitor and measure the intensity of nociception to quantify and treat it effectively. By controlling the magnitude of nociception, we can prevent it and reduce the need for opioids during or after surgery. The AlgiScan has been proven to be an effective monitor that fulfils these goals in clinical practice.
I can see that AlgiScan provides a unique feature of predicting the response to a nociceptive stimulus. This helps in adjusting morphinics doses before and during surgery or preparing for postoperative analgesia, based on an objective assessment of the patient’s response to infra-nociceptive stimulation. The most valuable aspect about using this monitor is the ability of the PPI mode to predict the reaction to a nociceptive stimulus.
TECHNICAL DATA

CLINICAL
- Measurements of patients’ analgesia level (PPI score, Tetanus,…)
- Pupil Reflex Dilation (PRD)
- Pupil size
- Photomotor reflex
ERGONOMICS
- Absolute measurements without calibration
- Wireless charging station
- Barcode scanning for patient identification
- Reusable or disposable eyecup
SPECIFICITY
- Stimulations : infra-nociceptive (PPI), Tetanos
- 320 Lux flash of light
- 0,1 mm precision
- Data transfer
- Opaque eyecup to impede ambient light

STANDARDS AND SAFETY
- EN60601-1 (Medical Electrical Equipment)
- EN60601-1-2 (EMC)
- IEC 62471 (Infrared light)
- IIA CE Class (CE 0549)
- Latex Free
Eco-friendly company

We are an
eco-friendly company

Open ended choice of
disposable or reusable material

Cost
control

Short production
cycle
PUBLICATIONS
They trust us

CONTACT US :











 CONTACT
CONTACT



